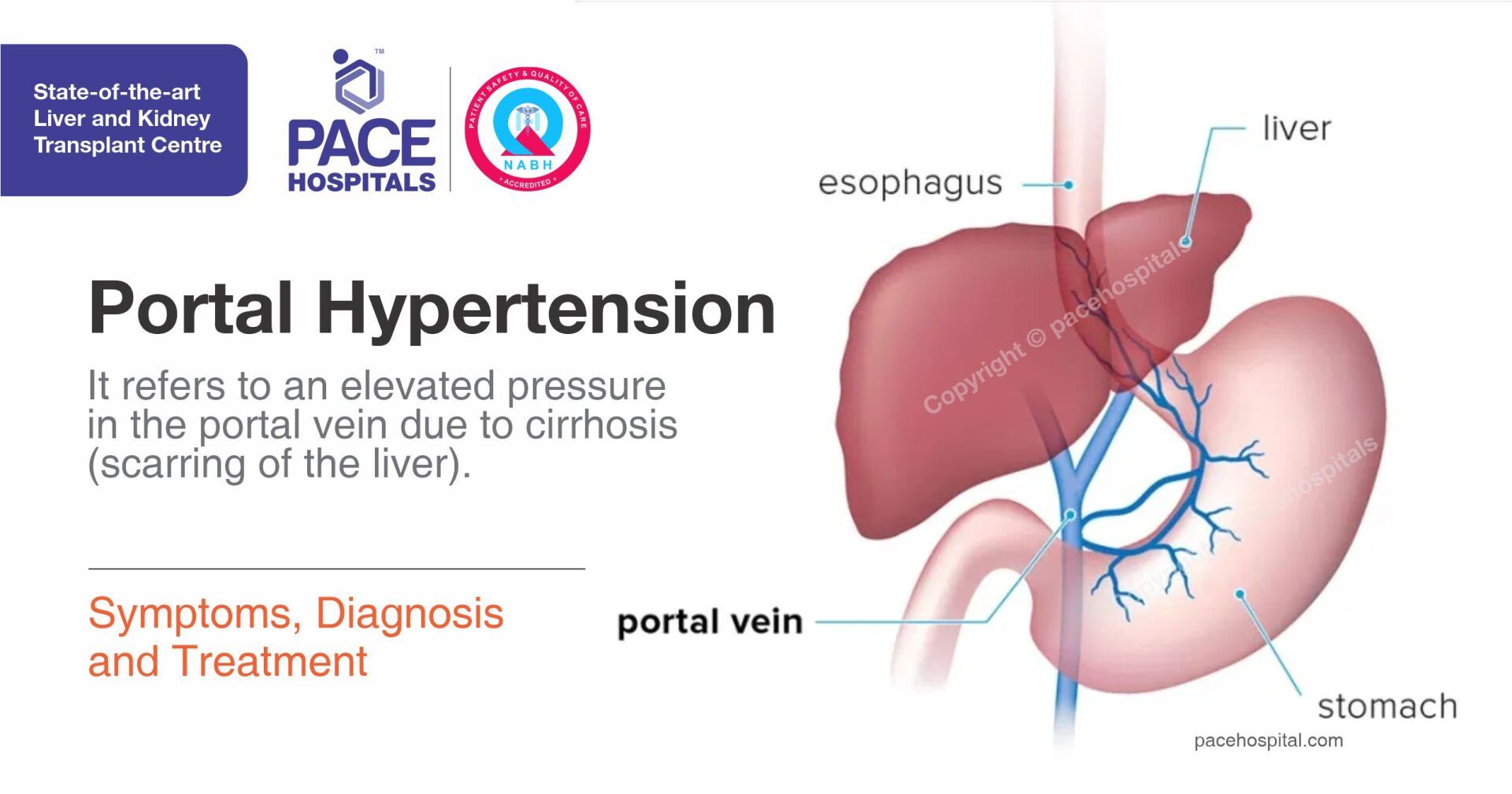
(Portal Hypertension) - Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Portal hypertension is an elevated pressure in the portal vein (veins that carry blood from stomach, intestine, spleen and pancreas to the liver). Elevated pressure is caused by blockage in blood flow through the liver. Increased pressure on portal veins causes large blood vessels (varies) to grow across the throat and the stomach to go around the blockage. The main cause of portal hypertension is cirrhosis (scarring of the liver).
Many times, people suffering from portal hypertension do not realize that there is a problem until they experience an episode of pain on one side of their body. This could be in the form of a dull ache or throbbing pain that spreads across the lower portion of the arm, or perhaps it happens when you flex your wrist.
- What are the Symptoms and Complications of Portal Hypertension?
Portal hypertension may not always be associated with specific symptoms identifying what is happening in the liver. But if you have a liver disease leading to cirrhosis, there are high chances of developing a portal hypertension.
Symptoms of portal hypertension are caused by complications of the bloodflow decreasing through the liver, and from increasing pressure in the vein. The main complications and symptoms of portal hypertension include:
- Gastrointestinal hemorrhage or bleeding is often the the initial presenting symptom of patients with portal hypertension. Blood vomiting, blood in the stool or Black, tarry stool due to bleeding and rupture from varices. These patients with advanced liver disease generally present with jaundice, ascites, coagulopathy, hepatic encephalopathy or spider nevus (spider angiomas), additional indication like enlargement of the spleen (splenomegaly) and dilated abdominal wall veins.
- Varices describes enlarged blood vessels. Blood, diverted to and gathered in another vein when heading to the heart. These varices can occur in the esophagus, stomach, around the umbilicus and in the anus and anal.
- Ascites is the end result of a series of events. Cirrhosis of the liver is the most common cause of ascites. When cirrhosis occurs, blood flow through the liver is blocked.
- Hepatic Encephalopathy is a decline in brain function (forgetfulness and confusion) that occurs as a result of severe liver disease. In this condition, your liver can’t adequately remove toxins from your blood. This causes a buildup of toxins in your bloodstream, which can lead to brain damage.
- Enlargement of the spleen (splenomegaly) often caused by infections, cirrhosis and other liver diseases, blood diseases characterized by abnormal blood cells, problems with the lymph system, or other conditions. Other causes of an enlarged spleen include: Inflammatory diseases such as sarcoidosis, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Decreased platelets levels and white blood cell counts increase the risk of general infection.
- How to diagnose of portal hypertension?
Generally Portal hypertension is diagnosed only after a complication like Gastrointestinal hemorrhage or bleeding, Jaundice, Ascites, Coagulopathy, Hepatic encephalopathy, Cirrhosis etc occurs.
It can be confirmed by Evaluation of your medical history, A physical examination, X-Ray, Blood tests, Ultrasound, CT Scan, MRI Scan and Endoscopy.
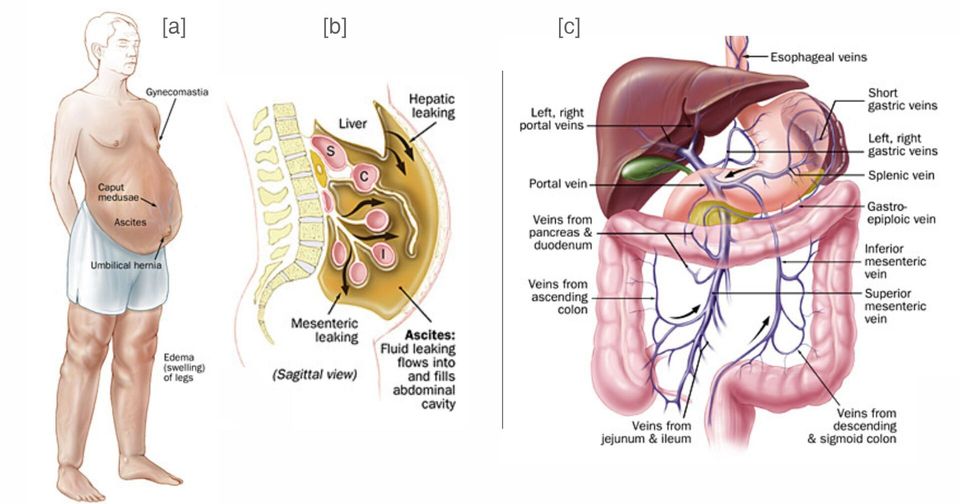
Figure 1 - [a] Clinical manifestations of portal hypertension. [b] Mechanism of ascites in portal hypertension; S=stomach; C=colon; I=intestine. [c] Anatomy of the portal venous system.
What are the treatment options for portal hypertension?
Treatment start with preventing complications of Portal hypertension. Once the complications identified, treating the underlying cause and alcohol abuse (due to the risk of further liver damage). It can be managed through diet, medications, endoscopic treatment, radiology or finally surgery. Treatment options are prescribed based on the symptoms severity and on how good your liver is working.
Lifestyle changes such as these can help treat portal hypertension:
- Dietary changes
- Avoiding alcohol intake
- Regular exercising
- Quitting smoking (if you smoke)
Acute bleeding from varices or nonvariceal sites in patients with portal hypertension requires prompt and appropriate measures to control bleeding and prevent recurrent episodes. Treatment is aimed at the prevention of recurrent episodes of variceal bleeding by lowering portal pressure and eliminating varices.
Medical Treatment: Medical management of bleeding esophageal or gastric varices may be instituted once the cause of the hemorrhage is documented to be variceal in origin. Drug treatment is aimed at reducing portal inflow, or collateral or intrahepatic resistance
Endoscopic Treatment: Endoscopy plays a vital role in the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Treatment options include sclerotherapy, banding of esophageal varices and balloon tamponade to control bleeding.
Banding: Acute variceal hemorrhage is ideally managed by variceal ligation with elastic rings. This is performed endoscopically, and is safe and effective.
Surgical Shunts: The aim of surgical shunting in portal hypertension is:
- to maintain hepatic and portal blood flow
- to reduce portal venous pressure
to try to reduce or not complicate hepatic encephalopathy
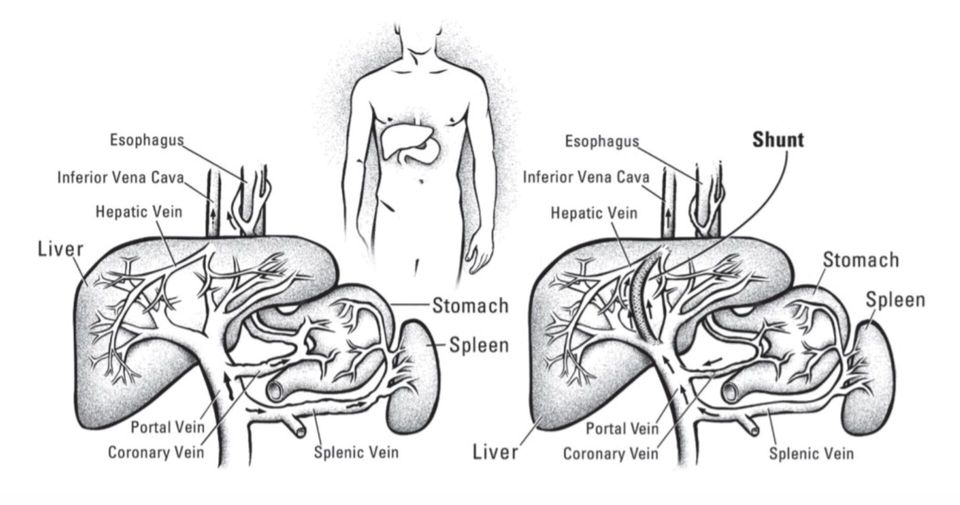
Figure 2 - Illustration of the placement of the transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) endoprosthesis between the portal vein and a hepatic vein
TIPS or TIPSS (Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt) is an artificial channel within the liver that establishes communication between the inflow portal vein and the outflow hepatic vein.
- An interventional radiologist creates the shunt using an image-guided endovascular (via the blood vessels) approach, with the jugular vein as the usual entry site. The procedure widely accepted as the preferred method for treating portal hypertension that is refractory to medical therapy, replacing the surgical portocaval shunt in that role. TIPS is a life-saving procedure in bleeding from esophageal or gastric varices. Figure 2 illustrates the generic placement of the shunt between the portal vein and a hepatic vein.
Liver Transplantation: Liver transplantation is the only effective treatment for end-stage liver disease. This option offers excellent patient survival and rehabilitation. Challenges of liver transplantation include a scarcity of human cadaver donors, rejection, and the limited financial resources of most patients.
Complications secondary to portal hypertension can be life threatening and are often the main indication for transplantation in patients with advanced liver disease.
References:
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt, "New non-operative treatment for variceal haemorrhage" [1] [2]
- Figure 1 Clinical manifestations of portal hypertension. Mechanism of ascites in portal hypertension; S=stomach; C=colon; I=intestine. Anatomy of the portal venous system
- Figure 2 Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt: A Literature Review
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Our Locations
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
By clicking on subscribe now, you accept to receive communications from PACE Hospitals on email, SMS and Whatsapp.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals News
Thank you for subscribing. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
-

Payment in advance for treatment (Pay in Indian Rupees)
For Bank Transfer:-
Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545
Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc)
Call us at 04048486868
ADDRESS
PACE Hospitals
Hitech City : Beside Avasa Hotel, Pillar No. 18, Hyderabad - 500081
Madinaguda: Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping, Madinaguda, Hyderabad - 500050
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals as such.